
Organizations are recognizing the need to modernize their management systems in order to remain competitive in today’s market. Studies indicate that traditional methods like annual appraisals are no longer effective and can, in fact, reduce employee engagement and motivation. Consequently, an increasing number of companies are adopting performance management practices. This dynamic and strategic approach to enhancing employee performance is gaining traction across companies of varying sizes, including numerous Fortune 500 and industry-leading organizations.
Performance management is a strategic approach aimed at enhancing employee performance, ultimately leading to increased company effectiveness. By concentrating on employee development and aligning organizational objectives with individual and team goals, managers can cultivate a work environment conducive to the success of both employees and the company.
In contrast to other methods of evaluating employee performance, such as annual performance reviews, performance management is a more dynamic and comprehensive process that yields superior results.
Benefits of Dynamic Performance Management
- Offering Timely Performance Insights: Dynamic performance management offers the advantage of providing up-to-the-minute performance feedback, allowing organizations to have a current and accurate view of how their employees are performing in real time.
- Maintaining Goals That Are Current, Transparent, and Aligned: One of the benefits of dynamic performance management is the ability to ensure that goals remain up-to-date, transparent, and closely aligned with organizational objectives. This keeps employees focused on what truly matters and enhances overall performance.
- Boosting Employee Engagement: Dynamic performance management plays a crucial role in elevating employee engagement. Through continuous feedback, skill development, and growth opportunities, employees are more likely to feel motivated, connected, and committed to their work and the organization.
- Enhancing Talent Retention: An important outcome of dynamic performance management is its positive impact on talent retention. By consistently supporting, recognizing, and developing employees, organizations can increase the likelihood of retaining valuable talent, reducing turnover.
- Cultivating Internal Leadership Development: Dynamic performance management actively fosters the growth of leaders from within an organization. By identifying and nurturing talent through ongoing assessments and coaching, companies can establish a robust leadership pipeline.
- Promoting Transparent and Candid Communication: Encouraging transparent and open communication is a hallmark of dynamic performance management. It facilitates constructive conversations, allowing employees and managers to address challenges, share feedback, and collaborate more effectively.
In practice, performance management involves ongoing efforts by management to nurture employee growth, establish clear objectives, and provide regular feedback throughout the year.
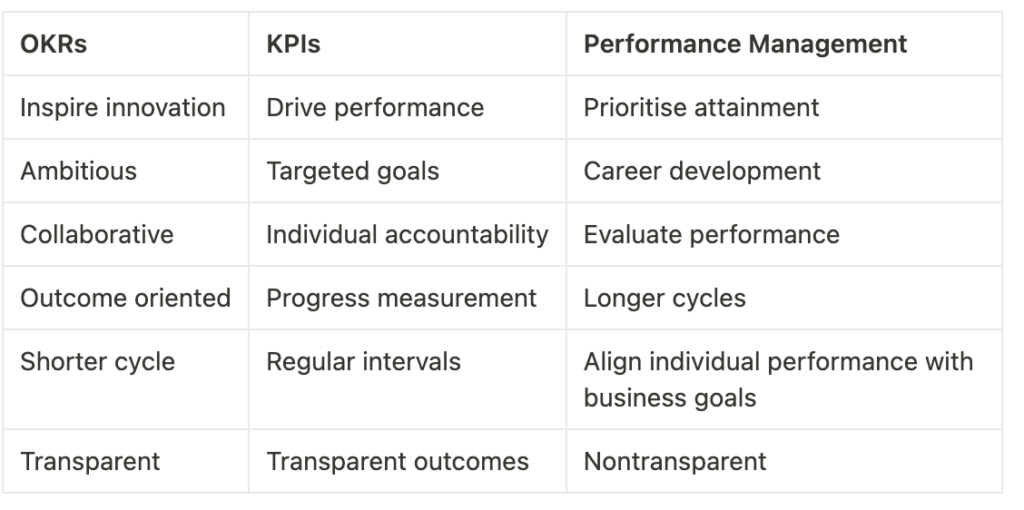
For establishing clear goals every organization requires objectives to fulfill its strategies and aspirations, and various goals and frameworks exist to track their journey towards these aims. You might be familiar with terms like OKRs and KPIs, and you may even be employing one or both of these methods in your goal-setting practices. It’s natural to wonder about their differences and how they relate to each other, especially if you’re more accustomed to one over the other.
Rest assured, you’re not the only one pondering these distinctions. A prevalent misunderstanding is that OKRs and KPIs are identical or can be used interchangeably, but this isn’t true — they represent two distinct types of goals. This article aims to address some frequently asked questions:
What exactly are OKRs and KPIs?
And what about Performance Management? How do OKRs and KPIs complement each other in practice? What benefits are there in monitoring OKRs and KPIs together, and how can they be leveraged in
What is a KPI?
KPIs are quantifiable metrics that provide critical insights into how effectively a company is achieving its key objectives, enabling leaders to make informed decisions.
What is an OKR?
OKRs, meanwhile, are a goal-setting framework designed to set and track ambitious, measurable goals, thus driving organizational alignment and engagement.
What is Performance Management?
Performance management is a systematic process focused on continuously improving organizational efficiency and effectiveness through the development and alignment of individual and team performances. It encompasses a range of activities including setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, conducting performance appraisals, and implementing development strategies. This approach aims to enhance employee engagement and productivity, aligning their skills and contributions with the company’s strategic objectives. Effective performance management creates a structured environment where employees are motivated and equipped to perform at their best, directly contributing to the overall success of the organization.
How can you include both OKRs and KPIs in your Performance Management?
OKRs are like big, exciting goals that encourage teams to be creative and try new things. It’s okay if they don’t always succeed because it’s part of the learning process. Instead of making OKRs the primary focus of annual performance reviews and promotion decisions, they are most effective when managed continuously. OKRs are dynamic and aspirational, capable of adapting as new information emerges over quarters. They facilitate an ongoing process of refinement and enhancement.
On the other hand, performance management goals are more about making sure employees do their jobs well and can affect their pay and promotions. Sometimes, this makes employees set easier goals to play it safe.
To avoid this, it’s better to use OKRs for innovation and performance management for regular job tasks separately, instead of mixing them up. This can help employees and the company perform better.
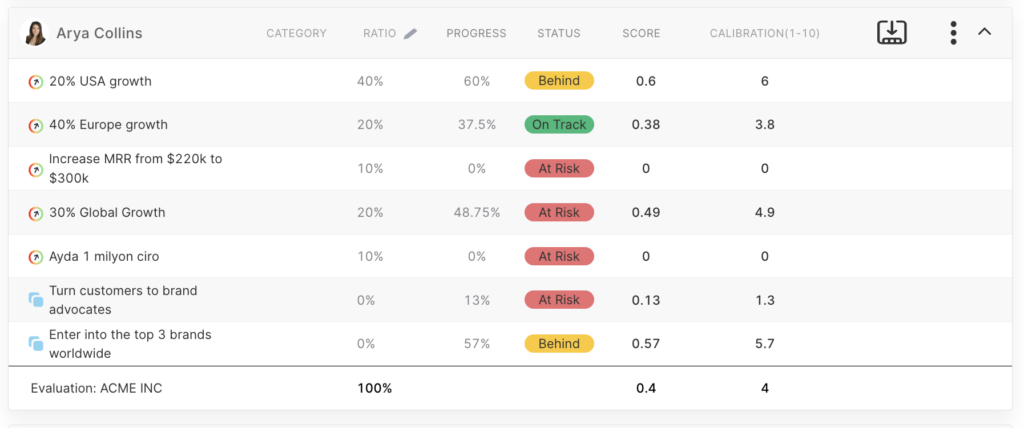
This doesn’t mean that you should keep OKRs completely separate. You can choose to add your OKRs to your goal cards and give them very low or no points to avoid affecting your performance score. During performance reviews, you can also discuss the OKRs on your goal cards, ensuring that OKRs are not entirely independent of performance management but still encouraging employees to set high goals.
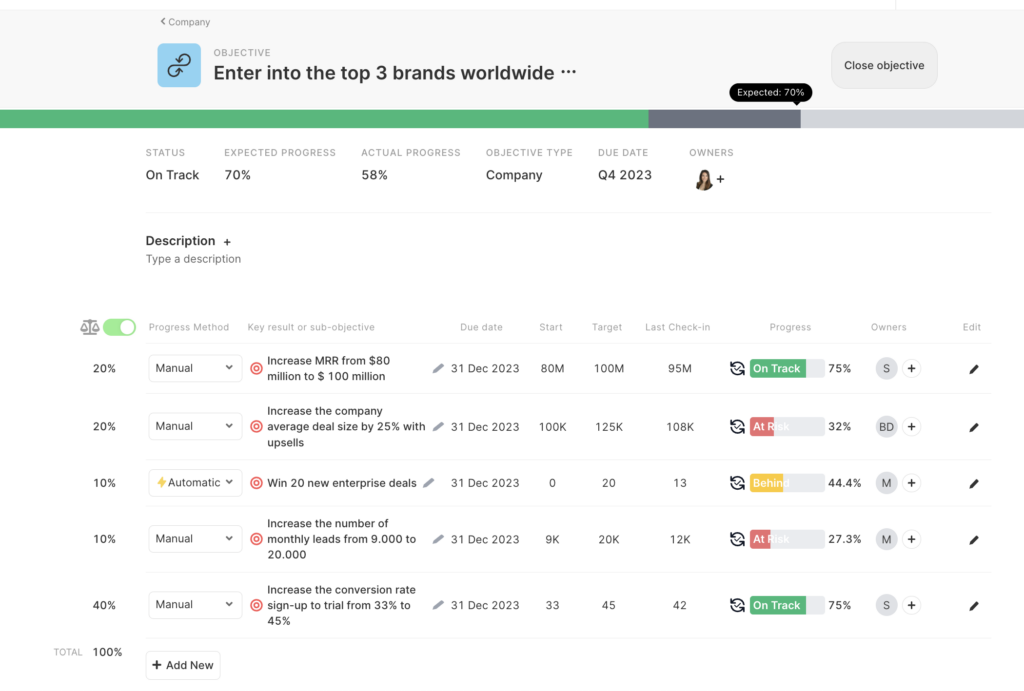
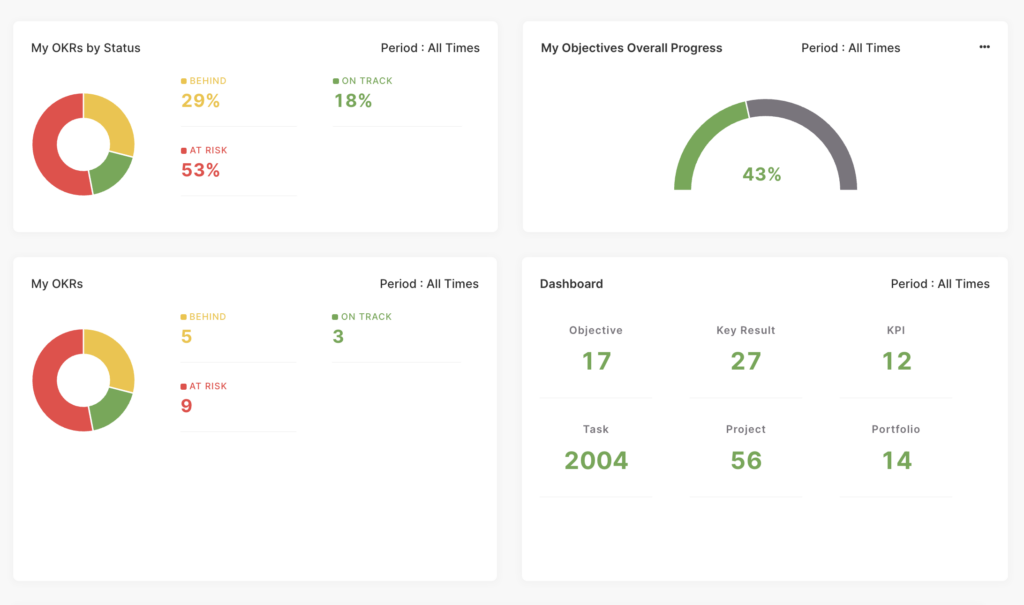
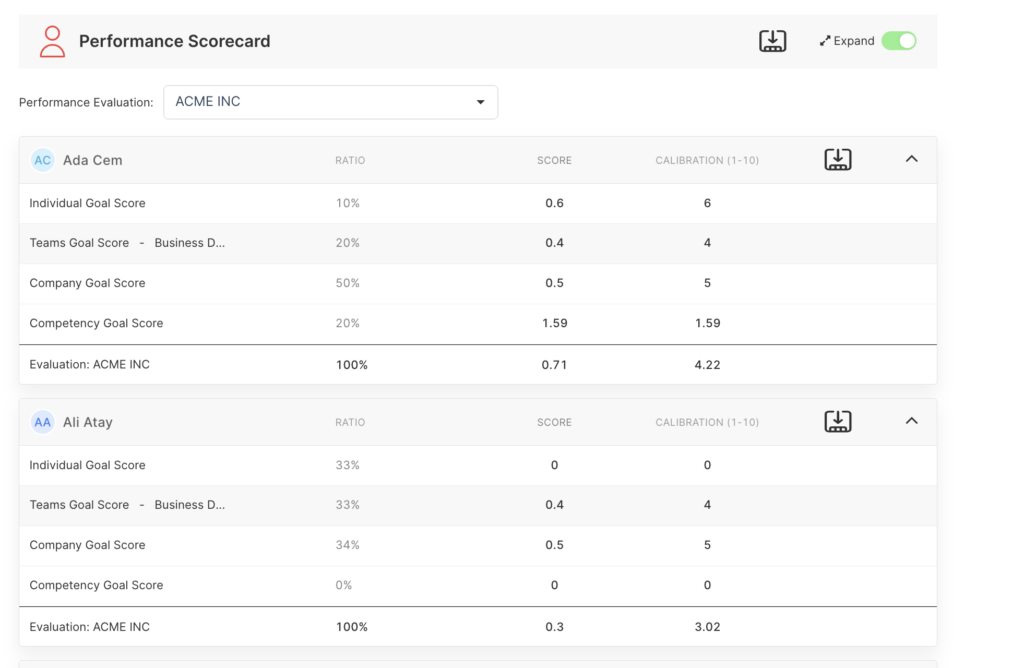
In this example, as you can see, key performance indicators (KPIs) carry a 100% weight on the individual card, while the impact of OKRs on performance is 0; however, you can still track them on the performance card.
According to Gallup “When organizations successfully engage their customers and their employees, they experience a 240% boost in performance-related business outcomes compared with an organization that has neither engaged employees nor engaged customers.”
So then, where to start?
Dynamic performance management involves a flexible and continuous approach to managing and improving employee performance. While the specific steps can vary depending on the organization’s needs and objectives, here are some common elements of dynamic performance management:
1. Setting Clear Goals: Start by defining clear and specific performance expectations and goals. Ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities and how their work contributes to the organization’s objectives.
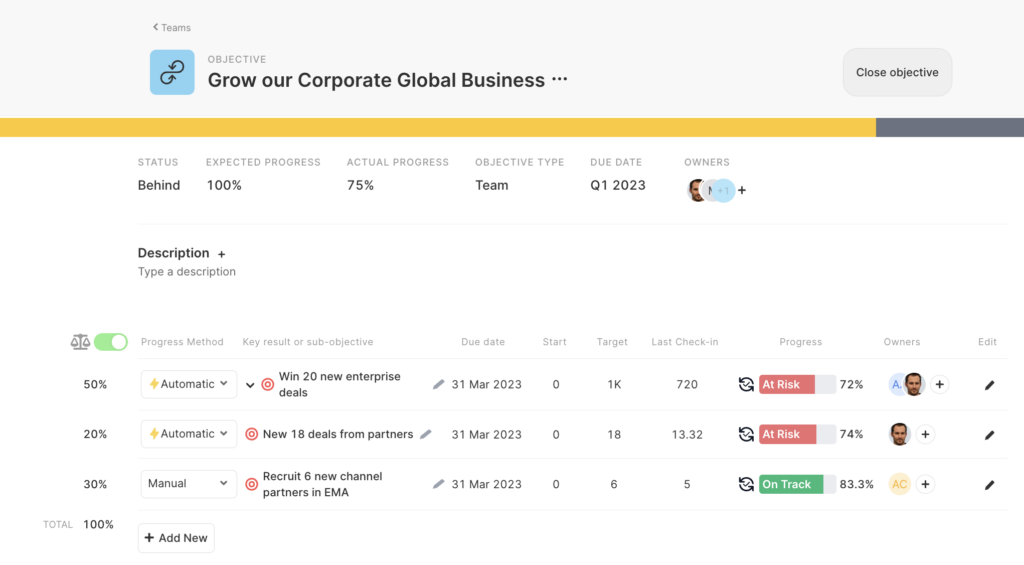
2. Continuous Goal Alignment: Regularly align individual and team goals with the company’s strategic goals. These goals should be revisited and adjusted as needed to stay in sync with the evolving priorities of the organization.
3. Regular Check-Ins: Replace traditional annual performance reviews with frequent, ongoing check-ins between employees and managers. These conversations focus on progress, challenges, and development opportunities.
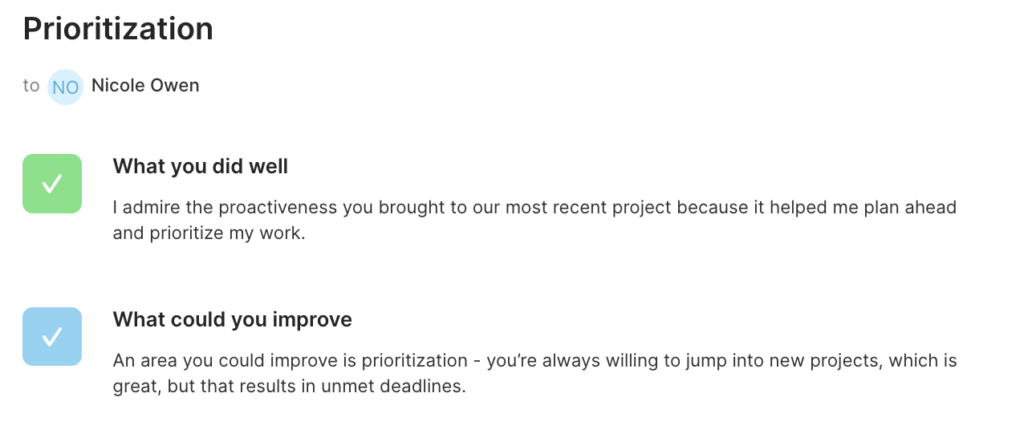
4. Feedback and Coaching: Provide continuous feedback to employees on their performance. Encourage a coaching and mentoring approach to help employees grow and develop their skills.
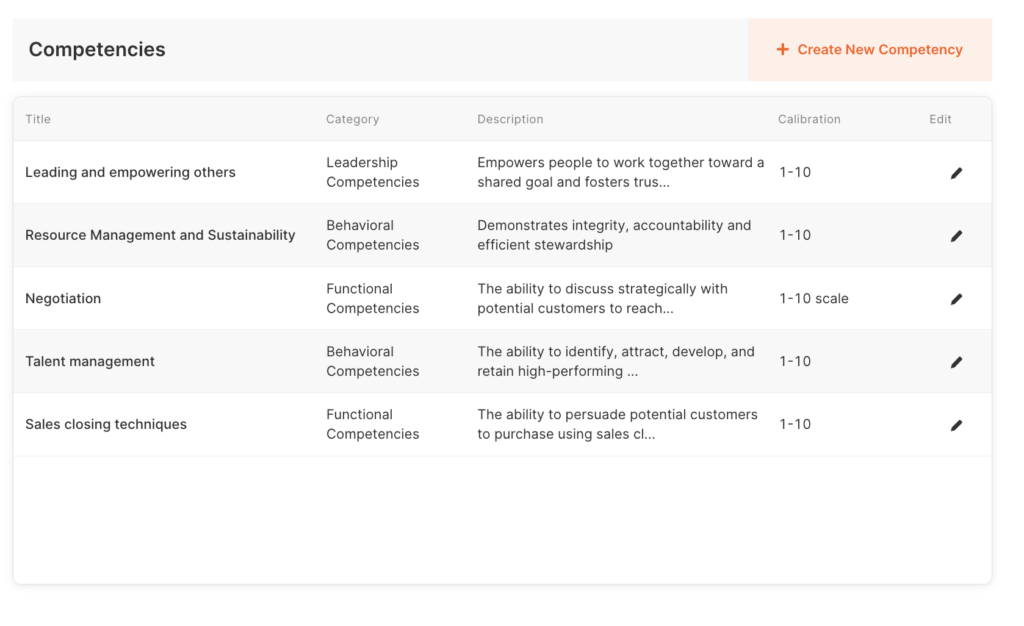
5. Skill Development: Identify areas where employees need improvement and provide targeted training and development opportunities. This can include on-the-job learning, workshops, or additional resources.
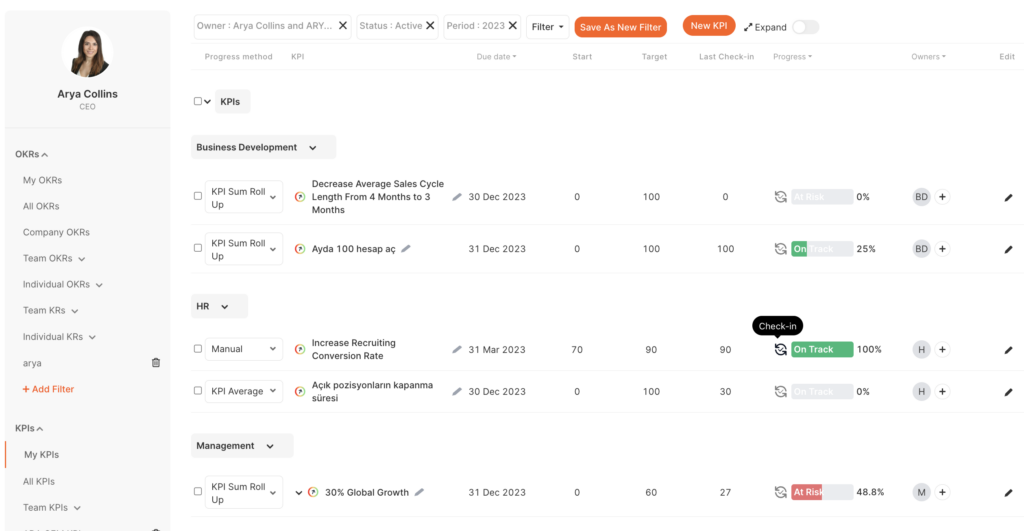
6. Data-Driven Insights: Utilize data and analytics to gain insights into employee performance trends and identify areas for improvement. Data can help inform decisions and strategies for enhancing performance.
7. Career Development: Encourage employees to discuss their long-term career goals and provide opportunities for advancement within the organization. This can involve succession planning and leadership development programs.
8. Recognition and Rewards: Recognize and reward employees for their achievements and contributions. This can be done through both formal and informal methods, such as peer recognition programs or bonuses.
As organizations navigate the ever-evolving landscape of modern business, it becomes evident that dynamic performance management is a critical strategy for achieving success.
Remember that dynamic performance management emphasizes ongoing dialogue, agility, and a focus on employee development, making it a more modern and effective approach compared to traditional, static performance reviews.
To learn more about how to manage OKRs, KPIs, and performance management, feel free to
To achieve scalable growth, it is essential to have the ability to collect, view, and analyze all relevant data in one centralized location. ConectoHub prioritizes providing a comprehensive solution that empowers fast-growing companies to manage all aspects of their operations and people management from a single platform. With ConectoHub, you can gain instant insights into every detail of your company.
Ready to take your company’s growth to the next level? Experience the transformative power of ConectoHub today and streamline your performance and work management processes. Don’t miss out—start your free trial now and see the difference ConectoHub can make!
